Monastery Of Manuel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kefeli Mosque ( tr, Kefeli Câmîi, meaning "the mosque of the Caffariotes", after the inhabitants of the city of
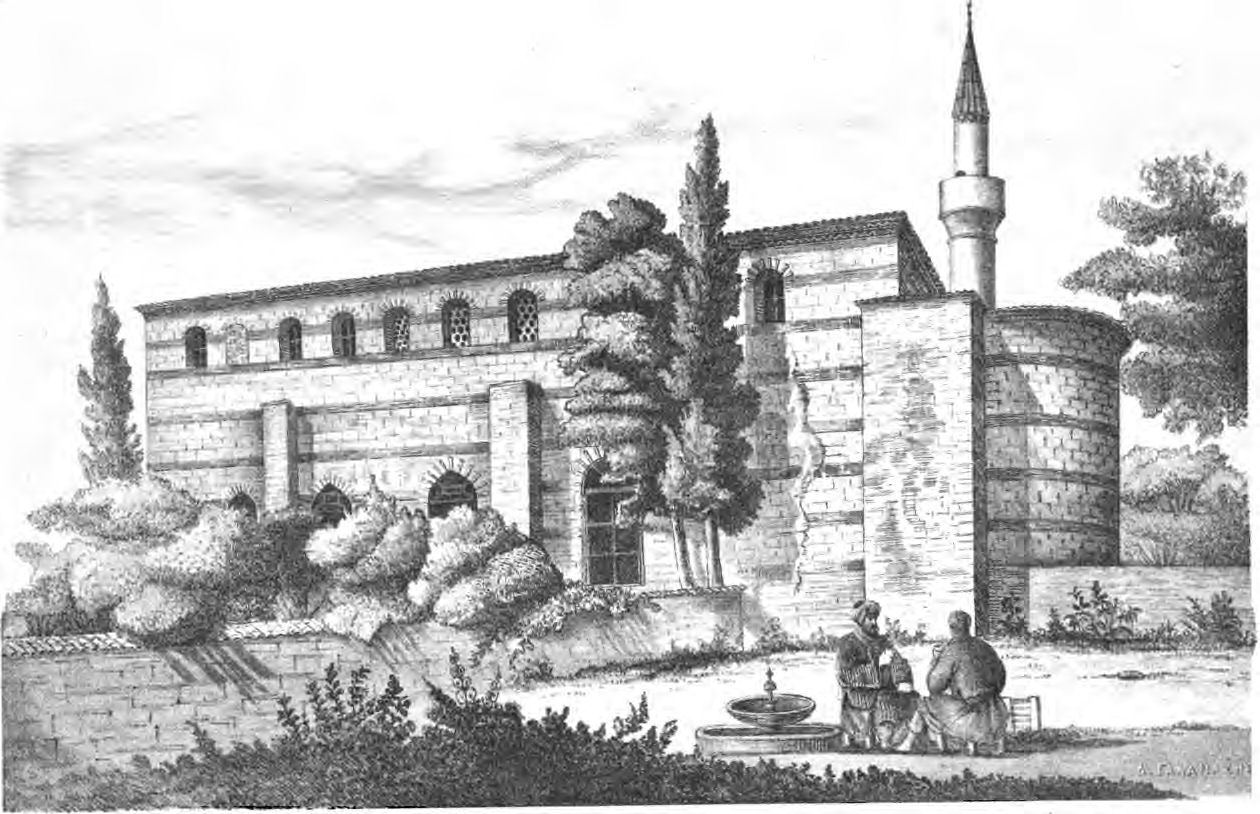 The origin of this building, which lies on the slope of the sixth hill of
The origin of this building, which lies on the slope of the sixth hill of
 The building is a large hall, 22.6 meter long by 7.22 wide,Van Millingen (1912), p. 258. and is oriented in north–south direction, which is quite uncommon among the Byzantine churches in
The building is a large hall, 22.6 meter long by 7.22 wide,Van Millingen (1912), p. 258. and is oriented in north–south direction, which is quite uncommon among the Byzantine churches in
Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
in Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, or also ''Kefeli Mescidi'', where ''Mescit'' is the Turkish word for a small mosque) is a former Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
church, later jointly officiated by Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
s and Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
s, and finally converted into a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
by the Ottomans. The Catholic Church was dedicated to Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-da ...
. Its date of dedication as an Eastern Orthodox church is unknown, but it is commonly identified with the 9th-century Monastery of Manuel ( gr, Μονὴ τοῦ Μανουήλ).
The interest of Kefeli Mosque arises because it repurposes the early Christian basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
form during the later Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
period.Mathews (1976), p. 190.
Location
The building lies inIstanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
, in the district of Fatih, in the neighborhood of Salmatomruk, on ''Kasap Sokak'', more or less halfway between the mosque of Chora and the mosque of Fethiye
Fethiye () is a city and district of Muğla Province in the Aegean Region of Turkey. It is one of the prominent tourist destinations in the Turkish Riviera. In 2019 its population was 162,686.
History
Fethiye was formerly known as Makri (). ...
.
History
 The origin of this building, which lies on the slope of the sixth hill of
The origin of this building, which lies on the slope of the sixth hill of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, is not certain. The tradition says that in the ninth century Manuel the Armenian
Manuel the Armenian (Medieval Greek, Greek: Μανούηλ ό Άρμένιος), was a prominent Byzantine Empire, Byzantine general of Armenians, Armenian origin, active from circa 810 until his death. After reaching the highest military ranks, ...
, a general in the wars
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
against the Saracens during the reign of Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Theophilos (r. 829–842), built a monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
converting his house, which lay near the cistern of Aspar
The Cistern of Aspar ( gr, ἡ τοῦ Ἂσπαρος κινστέρνη) or Great Cistern ( el, μεγίστη κινστέρνη), known in Turkish as Sultan Selim Çukurbostanı ("sunken garden of Sultan Selim"),Müller-Wiener (1977), p. 279 ...
. Manuel was the uncle of Empress Theodora
Theodora is a given name of Greek origin, meaning "God's gift".
Theodora may also refer to:
Historical figures known as Theodora
Byzantine empresses
* Theodora (wife of Justinian I) ( 500 – 548), saint by the Orthodox Church
* Theodora o ...
, wife of Theophilos, and before retiring to his monastery he was one of the three counselors who assisted her in the regency for her infant son Michael III, following the death of her husband.
The Monastery of Manuel was rebuilt by Patriarch Photius, and was restored again by usurper Romanos I Lekapenos
Romanos I Lekapenos ( el, Ρωμανός Λεκαπηνός; 870 – 15 June 948), Latinized as Romanus I Lecapenus, was Byzantine emperor from 920 until his deposition in 944, serving as regent for the infant Constantine VII.
Origin
Romanos ...
(r. 920–944). Emperor Michael VII (r. 1071–1078) retired here after his deposition.Van Millingen (1912), p. 257 All these events show the importance of this monastery in Constantinople. Nevertheless, the attribution of this building to the complex founded by Manuel is far from certain, and has been denied by the newest research.
The documented history of the current edifice begins in 1475, shortly after the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
, when the Ottomans conquered the Genoese colony of Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
, in Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. All the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
inhabitants who lived in Caffa ("Caffariotes" or, in Turkish, ''Kefeli'') were then deported to Istanbul and relocated to this quarter. The Latins, mainly Genoese, were authorized to use this building as a church together with the Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
. The church, dedicated to Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra, ; la, Sanctus Nicolaus (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Myra in Asia Minor (; modern-da ...
, was officiated by the Dominicans, and kept by four Catholic families.Müller-Wiener (1977), 166 Armenians and Catholics had separated altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
s. This small church depended on the near Catholic ''Church of Saint Mary'', which later became the Odalar Mosque. In 1630, under the reign of Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Cons ...
(1623–1640), the church was converted into a ''mescit'' (a small mosque) by Great Vizier Receb Pasha, but retained the denomination, being first known as ''Kefe Mahalle
is an Arabic word variously translated as district, quarter, ward, or " neighborhood" in many parts of the Arab world, the Balkans, Western Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and nearby nations.
History
Historically, mahallas were autonomous social i ...
'', then as Kefeli Mescidi. In exchange, the Armenians got a Greek church in Balat.
Architecture
 The building is a large hall, 22.6 meter long by 7.22 wide,Van Millingen (1912), p. 258. and is oriented in north–south direction, which is quite uncommon among the Byzantine churches in
The building is a large hall, 22.6 meter long by 7.22 wide,Van Millingen (1912), p. 258. and is oriented in north–south direction, which is quite uncommon among the Byzantine churches in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
. Its masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
consists of alternate courses of brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
s and stones. The original building had a triple-nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
plan, but the only remains of the side aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parl ...
s belong to the end wall of the western one. To the north side there is an arch and a semicircular apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an ''exedra''. In ...
made of bricks, which outside has a polygonal shape. The walls of the apse are indented by two niche
Niche may refer to:
Science
*Developmental niche, a concept for understanding the cultural context of child development
*Ecological niche, a term describing the relational position of an organism's species
*Niche differentiation, in ecology, the ...
s. The main aisle has walls which are lighted by two ranges of windows, which are irregularly spaced. The southern wall is also lighted by two ranges of windows. The lower windows are much larger than the higher. The entrance is situated in the middle of the western wall. Under the western side there is a cistern, whose roof rests on three column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
s.
The dating of the edifice is uncertain. The polygonal apse and the niches in the apse are typical of the churches of Palaiologan
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; grc-gre, Παλαιολόγος, pl. , female version Palaiologina; grc-gre, Παλαιολογίνα), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greek ...
foundation. The building is architecturally interesting because it is an example of reproposition of the early Christian Basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
form during the later Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
period.
References
Further reading
* * * * {{Churches-Mosques in Istanbul Byzantine sacred architecture Fatih